Vector rHVT-F vaccine protects chickens and reduces shedding in opposition to an Indian genotype XIII Newcastle illness virus
Ranikhet (Newcastle) Illness is a extremely contagious viral an infection that impacts a really broad vary of birds, particularly chickens and different poultry species. It’s brought on by Newcastle Illness virus (NDV), which was not too long ago renamed as Avian orthoavulavirus serotype 1 of the Orthoavulavirus genus, Avulavirinae subfamily and Paramyxoviridae household. It may trigger totally different scientific indicators and lesions relying on the virulence of the virus and the susceptibility of the host. Moreover, Newcastle Illness as a consequence of velogenic NDV strains is a notifiable illness, and it is likely one of the primary limitations for worldwide commerce of poultry and poultry merchandise.
The early methods to categorise the NDV had been primarily based mostly on its organic properties, akin to pathogenicity, plaque formation, thermostability, analyses of structural polypeptides, and hemagglutination inhibition patterns utilizing monoclonal antibodies (Ballági-Pordani et al., 1996; Russel and Alexander, 1983). With the rising use of molecular methods in viral analysis, the information of the NDV genetic traits improved considerably and several other molecular classification methods have been successively proposed. They focused the floor F (fusion) protein gene sequence.
In 1996, Ballági-Pordani and associates instructed the classification of NDV isolates into six distinct genotypes (I to VI) based mostly on restriction fragment size polymorphism (RFLP) analyses. This method was validated and additional improved by phylogenetic evaluation of partial F gene sequence knowledge, and extra NDV genotypes have since been recognized (Herczeg et al., 1999; Lomniczi et al., 1998). Diel et al. (2012) proposed a unified and goal system based mostly on the phylogenetic topology, evolutionary distances, department assist and epidemiological independence. It grew to become extensively used and resulted within the identification of recent genotypes. Nevertheless, the uncoordinated naming, inadequate software of the factors, incorrect assignments, utilizing restricted/partial datasets known as for one more revision and a consortium of 29 World Group of Animal Well being reference laboratories for ND was established in 2014 to revise NDV classification system. Dimitrov et al. (2019) revealed the outcomes of such effort with an up to date classification system that has a complete of not less than 20 distinct genotypes (I to XXI), together with the three new class II genotypes.
The genotype XIII and its subdivisions have been detected in India, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Iran, but additionally in additional distant locations like South Africa, Zambia, Tanzania, and others. These viruses could cause excessive mortality with large haemorrhages, congestion and necrosis in numerous visceral organs, and lymphoid depletion (Khorajiya et al., 2015; Nooruzzaman et al., 2021). In India, the genotype XIII has apparently grow to be probably the most prevalent pressure inflicting huge financial issues to native producers. The mortality price brought on by NDV genotype XIII, with or with out co-infections with different respiratory pathogens, in layers, color broilers & yard chickens, can attain as much as 40 – 50% (Khorajiya et al., 2015; Gowthaman et al., 2019).
With such large influence on the Indian poultry sector, researchers, opinion leaders and producers have been on the lookout for methods to guard flocks in opposition to the destructive penalties of this an infection that actually contain adhering to strict biosecurity protocols and revising vaccination applications. This quick article summarizes the primary ever problem research utilizing an Indian genotype XIII NDV pressure in chickens that had been immunized with a vector rHVT-F vaccine.
The vector rHVT-F vaccine
The vector vaccine of the rHVT-F sort, commercially often called Vectormune ND, makes use of the herpes virus of turkeys (HVT) because the spine and by which genome the Fusion (F) gene of a genotype I, D-26 pressure of NDV has been inserted. Its design is exclusive by way of insertion web site, promoter, and origin of F gene. The HVT pressure used to hold and categorical the F gene has been identified for many years as a really protected and steady virus, used worldwide to vaccinate chickens in opposition to Marek’s illness. The pressure (FC-126) and passage stage chosen for the development of Vectormune ND guarantee an energetic replication in chickens and a powerful expression of the F gene that are key factors in terms of early onset of immunity and excessive safety price.
The F protein is the primary virulence issue of NDV; certainly, it’s current on the floor of NDV, permitting it to connect to and penetrate the goal cells. It’s on the identical time a key immunogen. On this method, if immunity is constructed up in opposition to F protein, then NDV can not infect cells and create harm.
The safety induced by Vectormune ND in opposition to totally different genotypes has beforehand been assessed by problem research performed in industrial broilers, layers, turkeys, and SPF chickens utilizing genotypes II, III, IV and sub-genotypes V.2, VII.1.1, VII.2, VIII and XII.1 (in keeping with the newest classification as proposed by Dimitrov and associates). In all circumstances, scientific safety reached as much as 90 – 100% with a big shedding discount (Paniago et al., 2016). This preliminary knowledge offered robust proof of the pliability of this vaccine assemble to deal with a variety of NDV strains, belonging to a wide selection of genotypes. The consistency of scientific safety and of great discount of virus shedding are important within the long-term prevention of this lethal illness. Due to the detection and large circulation of genotype XIII in India and in a number of different nations, it grew to become related to check the efficacy of Vectormune ND in opposition to it, because it has by no means been completed earlier than.
Supplies and strategies
The research was performed on the Indian Institute of Know-how (IIT), Guwahati, Assam, in collaboration with the Heart for Medical Biotechnology of the Maharshi Dayanand College (MDU), Rohtak, Haryana, India. Briefly, one-day previous industrial broilers, Cobb 430 breed, with reasonable stage of maternally derived antibodies in opposition to NDV of seven.5 log2 (HI titer) or 11,179 ELISA items (BioChek ELISA equipment), had been allotted in two teams. Twenty-two (22) birds had been vaccinated at hatch with the rHVT-F vaccine (0.2 ml, by subcutaneous route), whereas 10 birds had been saved as unvaccinated controls. No different ND vaccines had been used.
At 4 weeks of age, all birds had been challenged utilizing an Indian genotype XIII NDV pressure, NDV/Hen/Pandu/2015 (GenBank accession quantity KY774445), at a dose of 102 CLD50 /chook (0.1ml), by oculo-nasal route and so they had been each day monitored for 12 days after the problem. Oropharyngeal swabs had been taken at 2- and 4-days post-challenge (dpch) and the shedding was assessed by hemagglutination exercise (HA) in SPF embryonated eggs.
Outcomes
The vaccine induced 95% of safety in opposition to mortality and morbidity whereas all birds within the management group succumbed with the attribute indicators and lesions of NDV an infection inside 6 to 9 days (Determine 1).
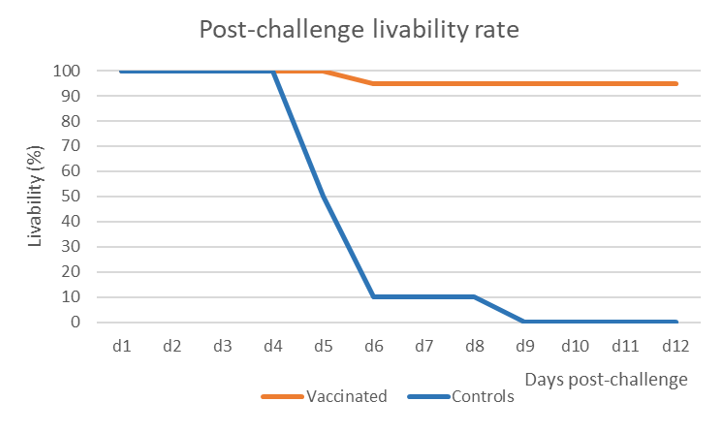
Oropharyngeal swabs had been taken at 2- and 4-days post-challenge (dpch) and the shedding was assessed by hemagglutination exercise (HA) in SPF embryonated eggs. This system doesn’t solely detect the virus, nevertheless it additionally assesses if the detected virus shed by the birds remains to be alive, opposite to the PCR which solely detects nucleic acid. Serial dilutions of the inoculum in eggs allow quantifying the HA exercise and the outcomes are expressed in Determine 2.
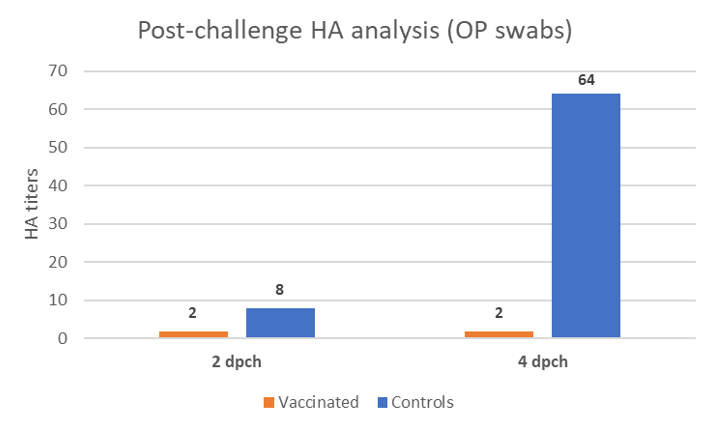
At 2 dpch, birds vaccinated with the rHVT-F vaccine already confirmed a slight discount within the re-excretion of the problem virus by the oropharyngeal route. At 4 dpch, chickens from the management group shed significantly greater quantity of virus whereas the vaccinated group remained re-excreting very low ranges of the genotype XIII virus.
Examine conclusions
The outcomes of this problem research demonstrated that Vectormune ND induced very robust scientific safety in opposition to the genotype XIII NDV pressure from India with important discount of the re-excretion of the problem virus.
From the sensible perspective, associating strict biosecurity procedures with a vaccination program together with Vectormune ND vaccination within the hatchery (both at day-old, or by in-ovo
route) offers the required safety for broilers. Moreover, because of its lengthy period of immunity (Palya et al., 2014) as a consequence of HVT persistence within the chook, this vaccine turns into a really handy answer for long-lived birds as effectively.
Because it was demonstrated by Tatár-Kis and associates, Vectormune ND reduces the transmission of Newcastle Illness virus in industrial broiler chickens (Tatár-Kis et al., 2020) (R<1). Likewise, the robust discount of the genotype XIII shedding proven on this research might contribute to include the unfold of this virus to neighboring flocks or close by farms. It may be thought to be a pretty choice for poultry producers in India and close by nations.
| References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Ballági-Pordany A., Wehmann E., Herczeg J., Belak S., Lomniczi B. | ||||
| (1996) | Identification and grouping of Newcastle illness virus strains by restriction web site evaluation of a area from the F gene.. Arch. Virol | 1996;141:243–261. | ||
| 2. Diel, D. G., da Silva, L. H., Liu, H., Wang, Z., Miller, P. J., & Afonso, C. L. | ||||
| (2012) | Genetic range of avian paramyxovirus sort 1: proposal for a unified nomenclature and classification system of Newcastle illness virus genotypes.. An infection, genetics and evolution : journal of molecular epidemiology and evolutionary genetics in infectious illnesses. |
12(8), 1770–1779. | ||
| 3. Dimitrov, Okay. M., Abolnik, C., Afonso, C. L., Albina, E., Bahl, J., Berg, M., Briand, F. X., Brown, I. H., Choi, Okay. S., Chvala, I., Diel, D. G., Durr, P. A., Ferreira, H. L., Fusaro, A., Gil, P., Goujgoulova, G. V., Grund, C., Hicks, J. T., Joannis, T. M., Torchetti, M. Okay., … Wong, F. Y. Okay. | ||||
| (2019) | Up to date unified phylogenetic classification system and revised nomenclature for Newcastle illness virus.. An infection, genetics and evolution: journal of molecular epidemiology and evolutionary genetics in infectious illnesses. |
74, 103917. | ||
| 4. Gowthaman, V., Singh, S. D., Dhama, Okay., Ramakrishnan, M. A., Malik, Y. P. S., Gopala Krishna Murthy, T. R., Chitra, R., & Munir, M. | ||||
| (2019) | Co-infection of Newcastle illness virus genotype XIII with low pathogenic avian influenza exacerbates scientific final result of Newcastle illness in vaccinated layer poultry flocks.. Virus illness |
30(3), 441–452. | ||
| 5. Herczeg J., Wehmann E., Bragg R.R., Dias P.M.T., Hadjiev G., Werner O., Lomniczi B. | ||||
| (1999) | Two novel genetic teams (VIIb and VIII) liable for current Newcastle illness outbreaks in southern Africa, one (VIIb) of which reached southern Europe.. Arch. Virol. | 1999;144:2087–2099. | ||
| 6. Khorajiya, J.H., Mathakiya, R.A., Joshi, B.P., Prajapati, Okay.S., Acharya, A., & Rajpura, R.M. | ||||
| (2015) | Isolation, identification, organic characterization and patho-epidemiology of genotype-XIII Newcastle illness virus outbreak in industrial vaccinated broiler farms.. Indian journal of poultry science, | 50, 132-137. | ||
| 7. Lomniczi B., Wehmann E., Herczeg J., Ballagi-Pordany A., Kaleta E.F., Werner O., Meulemans G., Jorgensen P.H., Mante A.P., Gielkens A.L., Capua I., Damoser J. | ||||
| (1998) | Newcastle illness outbreaks in recent times in western Europe had been brought on by an previous (VI) and a novel genotype (VII). Arch. Virol. | 1998;143:49–64. | ||
| 8. Nath, B., & Kumar, S. | ||||
| (2017) | Rising variant of genotype XIII Newcastle illness virus from Northeast India.. Acta tropica, |
172, 64–69. | ||
| 9. Nooruzzaman, M., Mumu, T. T., Kabiraj, C. Okay., Hasnat, A., Rahman, M. M., Chowdhury, E. H., Dimitrov, Okay. M., & Islam, M. R. | ||||
| (2021) | Genetic and organic characterization of Newcastle illness viruses circulating in Bangladesh throughout 2010-2017: additional genetic diversification of sophistication II genotype XIII in Southcentral Asia.. The Journal of basic virology, |
102(3), 10.1099/jgv.0.001554. | ||
| 10. Palya, V., Tatár-Kis, T., Mató, T., Felföldi, B., Kovács, E., & Gardin, Y. | ||||
| (2014) | Onset and long-term period of immunity offered by a single vaccination with a turkey herpesvirus vector ND vaccine in industrial layers.. Veterinary immunology and immunopathology, |
158(1-2), 105–115. | ||
| 11. Paniago, M., Gardin, Y., Palya, V., Cazaban, C., Lozano F., Tatár-Kis, T., Mató, T. Kiss, I. | ||||
| (2016) | Evaluation of the safety induced by a vector rHVT-F vaccine in opposition to totally different genotypes of Newcastle Illness virus. | In Proceedings of the sixty fifth Western Poultry Illness Convention (WPDC), p. 197-199. Vancouver, BC, Canada, April twenty fourth – twenty seventh, 2016. | ||
| 12. Russell P.H., Alexander D.J. | ||||
| (1983) | Antigenic variation of Newcastle illness virus strains detected by monoclonal antibodies.. Arch. Virol. | 1983;75:243–253. | ||
| 13. Tatár-Kis, T., Fischer, E. A. J., Cazaban, C., Walkó-Kovács, E., Homonnay, Z. G., Velkers, F. C., Palya, V., & Stegeman, J. A. | ||||
| (2020) | A Herpesvirus of Turkey-Based mostly Vector Vaccine Reduces Transmission of Newcastle Illness Virus in Business Broiler Chickens with Maternally Derived Antibodies.. Vaccines |
8(4), 614. |


