Be taught extra about nesting techniques
Editor’s observe: This text is an excerpt from the Cobb Breeder Administration Information and extra articles will observe. The Information was designed to spotlight essential components which are more than likely to affect flock efficiency. To learn or obtain the entire Information or to view Cobb’s different administration guides, click on right here.
Housing and tools necessities for group nesting techniques
Slats

Properly-designed slats are an integral a part of stopping flooring eggs. A ratio of 60 % flooring space to 40 % slat space is generally used. With a 12 m (40 ft) vast homes, slats want to increase 2 m (6.5 ft) from the entrance of the nest on all sides. With a 14 m (46 ft) vast homes, slats want to increase 2.7 m (8.8 ft) from the entrance of the nest on all sides. Apply a slat slope of seven° with hardwood or plastic slats. Hardwood slats are most well-liked when beginning with group nests as a result of there tends to be only a few slat eggs, females have improved grip to entry the nests and are cleaner than plastic slats.
Hardwood slats are additionally simpler for the caretakers to cross when checking the nests for mortality, cleanness and whether or not eggs are rolling accurately onto the belts. Don’t use mini-slats of 1.2 m (4 ft) vast which have solely sufficient area for a single drinker line. This technique may cause flooring eggs and have very inconsistent outcomes.
Feeders
A minimal of a single line or loop of the feminine feeder strains ought to be on or suspended above the slats. For a 12 m (40 ft) vast home, place 1 feeder line on the slats. In a 14 m (46 ft) vast home, place 2 feeder strains on the slats. The space from the slat step as much as the primary feeder ought to be a minimal of fifty cm (20 in).
Drinkers
The nipple drinker line in entrance of the nest should be 60 to 70 cm (23 1/2 to 27 1/2 in) from the nest entrance. The space between the water line and first feeder loop ought to be round 60 cm (23 1/2 in). Don’t put water strains within the scratch space for females. Drinkers ought to be put in at a fee of 8 to10 females per nipple or 1 bell drinker per 75 birds.
Lights
Lights ought to be positioned simply exterior the slat space and simply above the beginning of the litter (scratch) space, in order that the slats don’t solid a shadow over the scratch space. The scratch space ought to have uniform gentle distribution with excessive gentle depth (minimal 50 to most 100 lux). The lights ought to be situated to permit 2 to 4 lux to succeed in the again of the nest entrance. No additional lights inside or immediately above the nest are wanted.
Air flow
With respect to air flow, no air ought to undergo the nest and trigger draft which will be necessary when utilizing cross-ventilation. In tropical or sizzling climates, an excellent cooling system is required to forestall excessively excessive temperatures in the home and thus nests. Overheating in the home and nests will trigger females to put the eggs on the slats or scratch space. All the time use roof insulation with minimal R12 for tropical climates and R20 for chilly climates.
Housing and tools necessities for manufacturing techniques

Slat top is essential for welfare of the flock and for optimum efficiency outcomes. The advisable slat top (measured from the highest of the slats to the concrete flooring) is 45 cm (18 in). The 45 cm top is advisable as a result of droppings that fall by means of the slats will accumulate over time. If the slats are too low, the droppings could begin to contact the underside of the slats or come by means of the slats. If this occurs, the slats, nests, hen’s ft, and eggs can grow to be soiled and contaminated. For slats taller than 45 cm (not advisable) think about using steps, ramps or baskets positioned alongside the slat edge to facilitate fowl motion to and from the scratch space. Some slat designs have 2 top positions, considered one of 35 cm (14 in) used within the first a part of the manufacturing interval after which a second increased place of 45 cm used after 40 weeks of age. This idea is advisable for the Cobb females in group home setups (not US model home configuration that don’t supply this function).

Throughout home preparation and earlier than receiving birds in the home, conduct an in depth audit to make sure that slats are arrange accurately to optimize welfare outcomes. For instance:
- Are slats in good situation (no cracked, damaged or lacking slats), safe (hooked up to the braces beneath), and positioned accurately (spacing is suitable to forestall leg or foot entrapment)?
- Are the back and front boards securely hooked up to the slats to forestall fowl entrapment and entry beneath the slats?
- Are slats aligned accurately to forestall gaps and unevenness?
A course of audit for welfare is an efficient instrument to make use of through the switch course of to confirm that administration, dealing with, fowl care and biosecurity protocols are achieved. Examples of things to audit embody: home preparation and setup (lighting, drinker and feeder tools, slat situation, air flow, and so forth.), fowl situation and welfare high quality, dealing with through the unloading course of, calibration of feeding tools, upkeep of switch tools, and fowl conduct and distribution after switch.
Nesting techniques
Handbook nest techniques
Handbook nesting techniques are nonetheless widespread in areas of the world with decrease labor prices. These techniques ought to present 1 nest for 4 hens. The nest bins will need to have stable bottoms and be well-maintained so it’s the most engaging place in the home for the birds to put eggs. The nest ought to be fowl pleasant, have clear and dry bedding and supply environmental consolation for the hen. The best nest measurement is 25 cm (9 7/8 in) lengthy, 30 cm (11 7/8 in) excessive and 25 cm (9 7/8 in) deep, so females really feel protected. As well as, the instep ought to be not less than a 15 cm (6 in) excessive. Fill the nests with materials that could be a minimal 1/2 to a most 2/3 of the instep top for the hen to make a concave nest. Overfilling the nests will make them much less enticing and hens will kick out the costly nest materials. The utmost top to leap to the perches to get into the nest ought to be round 45 cm (18 in). Egg assortment ought to be accomplished continuously to forestall having greater than 3 eggs per nest as a result of this will induce pre-incubation and damaged eggs.

Mechanical nest or automated egg assortment
There’s a robust motion to mechanize egg gathering worldwide. The egg assortment in the home will be automated with particular person or group nests.
Particular person mechanical nest techniques
- Extremely popular within the USA home setup with 2/3 slats and 1/3 scratch space within the heart of the home.
- 1 line of mechanical nests on every of the slats or 2 strains of nests per home.
- The benefit of this design is a low share of flooring or slat eggs.
- All of the tools is over the slats (feeders, drinkers and nest system).
- Feminine density is restricted to a most of 5.5 females per m2 (1.96 ft2 per fowl). At this most density, a scarcity of feeder area can have an effect on peak manufacturing and manufacturing persistency.
Neighborhood nest techniques
- The business worldwide is adopting the European group nest system.
- 1 line of automated nests positioned within the central a part of the home with slats extending out from both facet of the nests.
- Feminine stocking densities: 6 to 7 females per m2 (1.54 to 1.80 ft2 per fowl).
- Increased feminine stocking densities considerably cut back hatching egg prices and pay for the upper funding prices resulting from increased monetary return per sq. meter.
- If the home design and tools configuration is right the group nest system is extremely environment friendly with a low share of flooring and slat eggs.
- For a system to achieve success, the nests should be very enticing to the females to forestall slat and flooring eggs.
Neighborhood Nest Design

With group nest techniques, there are usually 2 nest sizes (40 or 45 cm deep, by 240 cm lengthy) with every nest unit having 4 entrance holes, (2 on all sides). Use the suggestions on birds per nest gap from the producer or use the rules to the correct. Set up a nest system that offers the bottom share of flooring or slat eggs. All the time use the bigger nest dimensions when homes are 14 m or wider.
Most nest varieties available in the market don’t exceed 200 females per nest unit (nest unit of two.4 m size with 83 hens per linear meter of home). This calculation is conservative and can be utilized when starting an operation with group nests. There’s all the time the likelihood to extend the feminine density when the operation runs nicely and sufficient of expertise has been obtained.
Instance tips of hens per nest gap for Jansen and Van Gent nests*
40 cm deep nest – calculate most 230 females per nest unit (4 holes)
* or 58 females per gap
* or 96 females per linear meter of home size (48 females on all sides of the nest per linear meter of home size)
45 cm deep nest – calculate most 260 females per nest unit (4 holes)
* or 65 females per gap
* or 108 females per linear meter of home size (54 females on all sides of the nest per linear meter of home size)
*Producers named listed here are for guideline functions and shouldn’t be thought of as an endorsement.
Feminine density in manufacturing
In a 12 m vast home set up 3 chain feeder loops. This gives:
1200 cm of feeder area per meter home size ÷15 cm feeder area/hen = 80 hens per linear meter home size
80 hens per linear meter home size ÷ 12 m vast home = 6.7 hens/m2
For nest techniques going from the entrance to the again of the home with solely a cross over at each ends and one half-way in the home, the nesting area is ample for 80 hens per linear meter.
In a 14 m vast home set up 4 chain feeder loops, 2 on the slats and a couple of within the litter space. This gives:
1600 cm of feeder area per linear meter home ÷ 15 cm feeder area per hen = 107 hens per linear meter home
107 hens per linear meter home ÷ 14 m vast home = 7.6 hens /m2.
Usually density is restricted to 7 hens / m2 with good environmental situations. When utilizing solely 3 feeder loops the density will grow to be:
1200 cm of feeder area per linear m home ÷ 15 cm feeder area per hen = 80 hens per linear meter home
80 hens per linear meter home ÷ 14 m vast home = 5.7 hens /m2.
As a result of density is low, it’s higher to put in the 4th chain loop to have some flexibility with feeder area. An alternative choice is to start out out with 3 loops and 5.7 hens /m2 and, later, increase to 7 hens /m2. On this case, all the time set up the primary 2 feeder strains on the slats as it’s simpler to put in an extra feeder loop within the scratch space when growing from 3 to 4 feeder loops.
Growing hen density will be very useful by way of price (see desk to under). That is probably the most cost-effective strategy to enhance the monetary revenue per m2 of home space and the price of producing a hatching egg and chick.
When growing the feminine density, tools may even want to extend (feeder, drinker and nesting area). As talked about earlier, an excellent tunnel air flow system with pad cooling is essential to have the proper ambient temperatures and humidity to maintain the birds comfy and the litter or shavings in good situations.
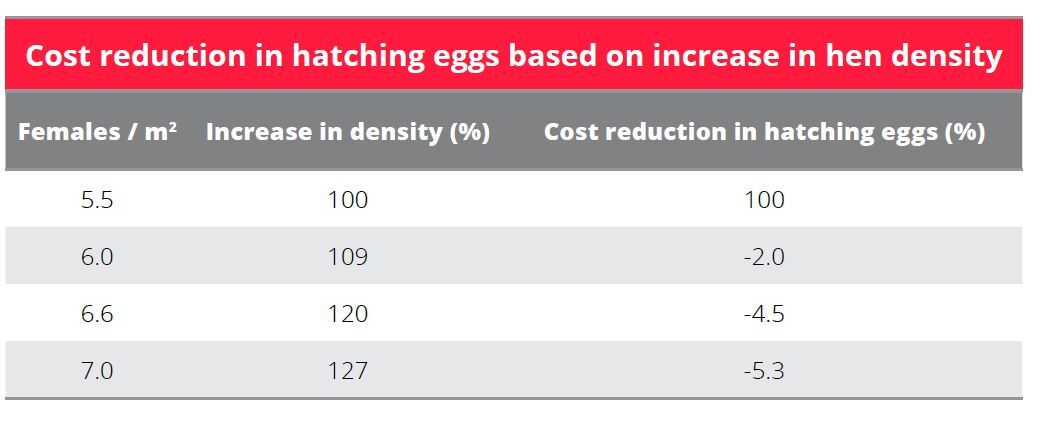
Neighborhood nesting techniques designs
Half of a 12 m vast home
Slats ought to be 45 cm excessive (adjustable between 35 and 45 cm). For a 12m vast home, the configuration has just one feeder line on the slats. There are 3 loops of chain feeders or 6 strains giving the potential density of 6.7 females per m2 with 15 cm of feeder area per fowl. Nipples are spaced 20 cm aside.
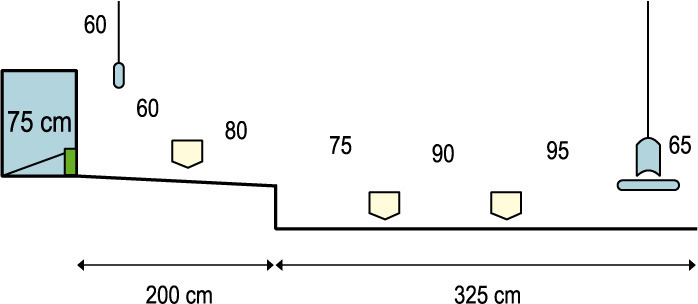
Half of a 14 m vast home with 3 feeder loops
Slats ought to be 45 cm excessive (adjustable between 35 and 45 cm). Slat slope of seven to eight levels. This configuration with 3 chain loops offers area for five.7 females per m2 with 15 cm of feeder area. With 2 chain loops on the slats, there may be lots of area within the litter space the place there may be just one chain loop. This retains the litter in higher situation than setups with 2 loops within the litter and gives extra space for mating.
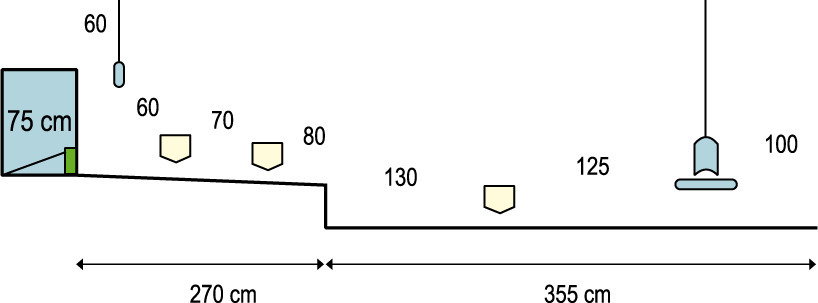
Half of a 14 m vast home with 4 feeder loops
Slats ought to be 45 cm excessive (adjustable between 35 and 45 cm). With 4 feeder loops, there may be feeder area for 7.6 females/m2 with 15 cm of feeder area per feminine. Nevertheless, in most climates, the utmost of seven females per m2is used. Increased densities are solely advisable in cooler (temperate) climates and/or with good environmental managed situations(pad cooling and tunnel air flow). With 4 chain loops, there may be 16.3 cm of feeder area per feminine.


