
Necrotic Enteritis (NE) happens in broilers as a consequence of an overabundance of C. perfringens and is often related to predisposing elements which embrace coccidial problem, poorly digested feed, and immune suppression. Coccidiosis is usually thought of a main predisposing issue for the onset of NE improvement in each industrial and analysis settings.
Multifactorial causes of Necrotic Enteritis
Coccidiosis results on mucosal permeability can result in plasma protein leakage into the intestinal lumen which may enhance intestinal pH, lower intestine motility, and enhance the potential for a secondary bacterial an infection. Eimeria spp. may enhance intestinal mucus manufacturing. Although mucus is a vital a part of the first barrier in opposition to invading pathogens, overproduction is a supply of vitamins for mucolytic micro organism together with Clostridium perfringens.
There was appreciable dialogue on which toxin(s) produced by C. perfringens is primarily answerable for NE in chickens. The toxin most frequently related to NE is the α-toxin, although Keyburn et al. (2006; 2008) questioned the unique α-toxin analysis and revealed a paper describing “NetB” as a brand new toxin that needs to be thought of. A evaluation by Rood et al. (2016) urged that the onset of NE is complicated, with a number of contributing elements, and never merely the presence of a particular toxin.
Clostridium Perfringens life cycle and calcium
Clostridium perfringens is a commensal bacterium that may exist within the gut and the setting (litter, soil, water, feces, meals, and so forth.). The life cycle of C. perfringens begins with a spore which is able to germinate underneath favorable circumstances right into a vegetative cell. The vegetative cell replicates and subsequently sporulates. A C. perfringens spore can survive for years and is proof against warmth, cleansing, and disinfectants.
The composition of the spore coating consists of parts that assist facilitate germination and these embrace Ca and dipicolinic acid. Latest in-vitro analysis has demonstrated that C. perfringens germination additionally requires exogenous calcium. This was beforehand demonstrated with C. difficile, a Clostridium species with implications for human well being. The presence of Ca within the gut (particularly at larger ranges) can theoretically circumvent the necessity for endogenous Ca and DPA from the spore coating.
As soon as a vegetative cell has fashioned, C. perfringens replicates through binary fission to supply two vegetative cells. The manufacturing of the α– and netB toxins happens when C. perfringens is a vegetive cell. When C. perfringens encounters enterocytes within the intestinal lumen it produces α-toxin. Greater concentrations of C. perfringens (109 CFU) and restricted nutrient availability stimulate NetB manufacturing by way of quorum sensing and each toxins make the most of Ca.
The third life stage, sporulation, leads to the formation of an endospore. The induction of sporulation can happen in response to elevated C. perfringens density and unfavorable circumstances corresponding to lack of vitamins. Although Ca just isn’t wanted for sporulation), elevated Ca throughout spore formation can enhance the protecting capability of the endospore. Spores with elevated Ca and DPA are extra proof against warmth and thus more durable to kill. Sporulation additionally responds positively to phosphorus within the intestinal setting because it counteracts the inhibitory results of glucose and subsequently facilitates sporulation.
Earlier analysis means that elevated Ca ranges within the weight loss plan will increase the exercise of each toxins leading to elevated NE mortality. Our speculation is that decreasing dietary Ca could lower mortality associated to NE by decreasing the supply of Ca wanted for a number of life phases of C. perfringens. Each hypotheses require extra analysis.
Results of Bacillus DFM’s in broilers with Necrotic Enteritis
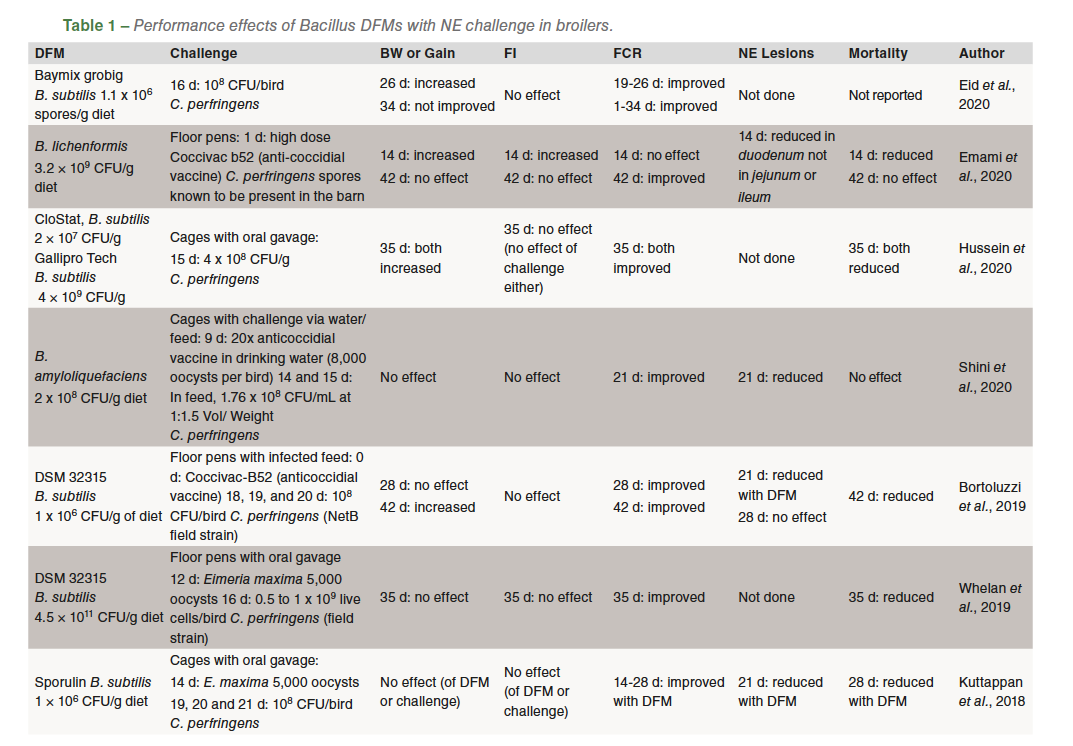
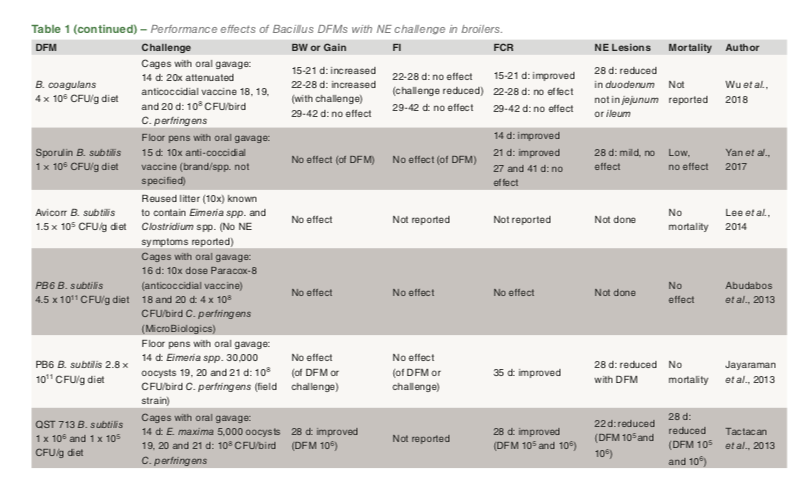
A abstract of revealed broiler research utilizing supplemental Bacillus DFMs with a NE problem are proven in Desk 1. These trials counsel an inconsistent impact of DFM on physique weight and achieve. Seven trials report no impact of the DFM whereas six present an enchancment in achieve. Within the six with improved achieve, three occurred within the part instantly after problem whereas the opposite three reported an total enchancment on the finish of the trial. This inconsistent impact of Bacillus DFM on physique weight and achieve is much like analysis research in birds that aren’t challenged. Feed consumption was not affected by DFM supplementation in earlier problem research (Desk 1) whereas in research with no problem feed consumption results of DFMs are inconsistent, some present no results, whereas some reveal enhancements which may be age or part dependent.
Bacillus DFM supplementation improves feed conversion ratio in most analysis trials with NE problem (Desk 1). 9 trials reported an enchancment whereas in three different research, there was no impact or enchancment was age dependent. In trials with out an NE problem, roughly half the research demonstrated no effectand the opposite half an enchancment of DFM on feed conversion ratio.
Eight research with broilers challenged with NE reported NE lesion severity scores (Desk 1). 5 reported decreased NE lesions with DFM, and two noticed decreased lesions within the duodenum however not within the ileum or jejunum. The one remaining trial reported no impact of DFM on lesions although all lesions have been famous as gentle. In 9 NE problem research the place mortality information was reported, there was decreased mortality with DFM supplementation in 5 research, three reviews with no impact and one with a transient impact however no total impact on the finish of the examine (Desk 1). In abstract, dietary DFM inclusion in broilers with NE seems to have a considerably optimistic impact on FCR. Bacillus DFMs could scale back NE lesions and mortality although results on BW and FI shouldn’t be anticipated, although transient results could happen in broilers affected by NE.
 Decreasing dietary calcium in broilers with Necrotic Enteritis
Decreasing dietary calcium in broilers with Necrotic Enteritis
As alluded to beforehand, there may be some analysis suggesting {that a} discount in dietary Ca ranges in broilers with NE could scale back mortality. Paiva et al. (2013) reported that mortality was decreased from 20% to five% in birds fed decreased Ca diets (0.9% vs 0.6%) at 21 days of age when supply of Ca was calcified seaweed and dicalcium phosphate. In birds fed Ca from limestone and dicalcium phosphate with comparable Ca variations, mortality was decreased from 12% to 7% at 21 days of age. In a second trial mortality was decreased from 20% in birds fed normal Ca diets to 10% in birds fed decreased Ca diets at 35 days of age. The Ca supply was calcified seaweed and dicalcium phosphate and normal or low dietary Ca therapies stepped down with age (starter: 0.9% or 0.6%, grower: 0.8% or 0.52%). The NE problem within the trials by Paiva have been from publicity to C. perfringens within the litter (from a earlier flock with NE) after reside coccidiosis vaccine.
Zanu et al. (2020) in contrast dietary Ca ranges utilizing an induced NE problem the place broilers got three Eimeria spp. on day 9 adopted by a NetB optimistic pressure of C. perfringens orally gavaged on days 14 and 15. Therapies have been normal or low dietary Ca that was stepped down with age (starter: 1% or 0.6%, grower: 0.9% or 0.5%, and finisher 0.8% or 0.4%). Mortality at 42 d was decreased from 7% in birds fed normal Ca diets to three% in these fed low Ca diets. Intestinal lesions have been larger in challenged broilers however there was no impact of Ca on lesion scores. Lesion scores weren’t decided by Paiva et al.
 Present dietary formulation makes use of complete Ca although formulating diets on digestible Ca values has not too long ago been reviewed by Stroll et al. (2021a). Limestone and different calcium sources can range in solubility. Extra particularly, as particle measurement will increase, solubility decreases in-vitro, and digestibility will increase in-vivo. In a trial with broilers from 0 to 10 days of age, diets have been formulated on digestible Ca. Tibia ash % was optimized in diets with near 0.5% digestible Ca (1.01% analyzed complete Ca). Although diets as little as 0.3% digestible Ca (0.64% analyzed complete Ca) didn’t considerably scale back tibia ash % when in comparison with the reference weight loss plan (0.89% analyzed complete Ca).
Present dietary formulation makes use of complete Ca although formulating diets on digestible Ca values has not too long ago been reviewed by Stroll et al. (2021a). Limestone and different calcium sources can range in solubility. Extra particularly, as particle measurement will increase, solubility decreases in-vitro, and digestibility will increase in-vivo. In a trial with broilers from 0 to 10 days of age, diets have been formulated on digestible Ca. Tibia ash % was optimized in diets with near 0.5% digestible Ca (1.01% analyzed complete Ca). Although diets as little as 0.3% digestible Ca (0.64% analyzed complete Ca) didn’t considerably scale back tibia ash % when in comparison with the reference weight loss plan (0.89% analyzed complete Ca).
Combining a number of dietary approaches to cut back Necrotic Enteritis in broilers
A analysis trial was accomplished by Calvert et al. (2015) which included three dietary Ca ranges (0.90%, 0.75% and 0.60%; from limestone and dicalcium phosphate) with or with out a Bacillus subtills DFM. The NE problem utilized the identical technique as Paiva which was publicity to C. perfringens within the litter (from a earlier flock with NE) after administering a reside coccidiosis vaccine on the really useful dosage. Mortality associated to NE at 28 d was decreased from 16% to six% when dietary Ca degree was decreased from 0.90% to 0.60% (P≤0.05).
Mortality in broilers fed 0.75% dietary Ca was intermediate at 10%. Feed consumption was depressed as dietary Ca degree elevated possible as a result of extra extreme NE problem current in broilers fed larger ranges of Ca. Physique weight and achieve have been improved in broilers fed the DFM with 0.60% dietary Ca in comparison with broilers fed the 0.90% dietary Ca with out DFM (P≤0.05). No impact on feed conversion ratio occurred associated to both Ca degree or DFM supplementation. That is possible as a result of elevated variability given the pure NE problem that was utilized on this trial in comparison with most earlier trials with DFMs which have utilized recognized quantities of C. perfringens administered to every hen.
Ileal Ca digestibility was decreased as dietary Ca elevated from 0.60% to 0.90%. P.c tibia ash was not totally different between 0.6% and 0.75% Ca diets although it was larger in chicks fed 0.75% Ca versus these fed 0.90% Ca at 18 days (P≤0.05). Throughout an NE problem it seems that chicks could regulate Ca absorption and utilization to forestall indicators of deficiency.
Decreasing dietary Ca degree decreased mortality associated to NE and when mixed with a Bacillus DFM improved physique weight achieve. Decreasing Ca ranges in diets to under trade requirements could also be one dietary method to handle the severity of NE although it might not be enough to enhance efficiency with out using different strategies as demonstrated on this trial by the inclusion of a DFM with decrease Ca diets.
References out there on request
From the Proceedings of the Midwest Poultry Federation Conference 2022


