Growth to a brand new mammal species is regarding
Scientists are on alert for modifications within the H5N1 or fowl flu virus that might sign it’s adapting to unfold amongst people. The virus has induced critical, typically deadly, infections amongst folks and has lengthy been on the checklist of viruses with pandemic potential. Any growth to a brand new mammal species is regarding.
An outbreak of fowl flu amongst cattle herds in the USA led to the primary recognized case of transmission between a cow and a human, after a Texas farm employee caught the virus. Beforehand, the virus had largely been handed to people by means of shut contact with wild birds or contaminated poultry.
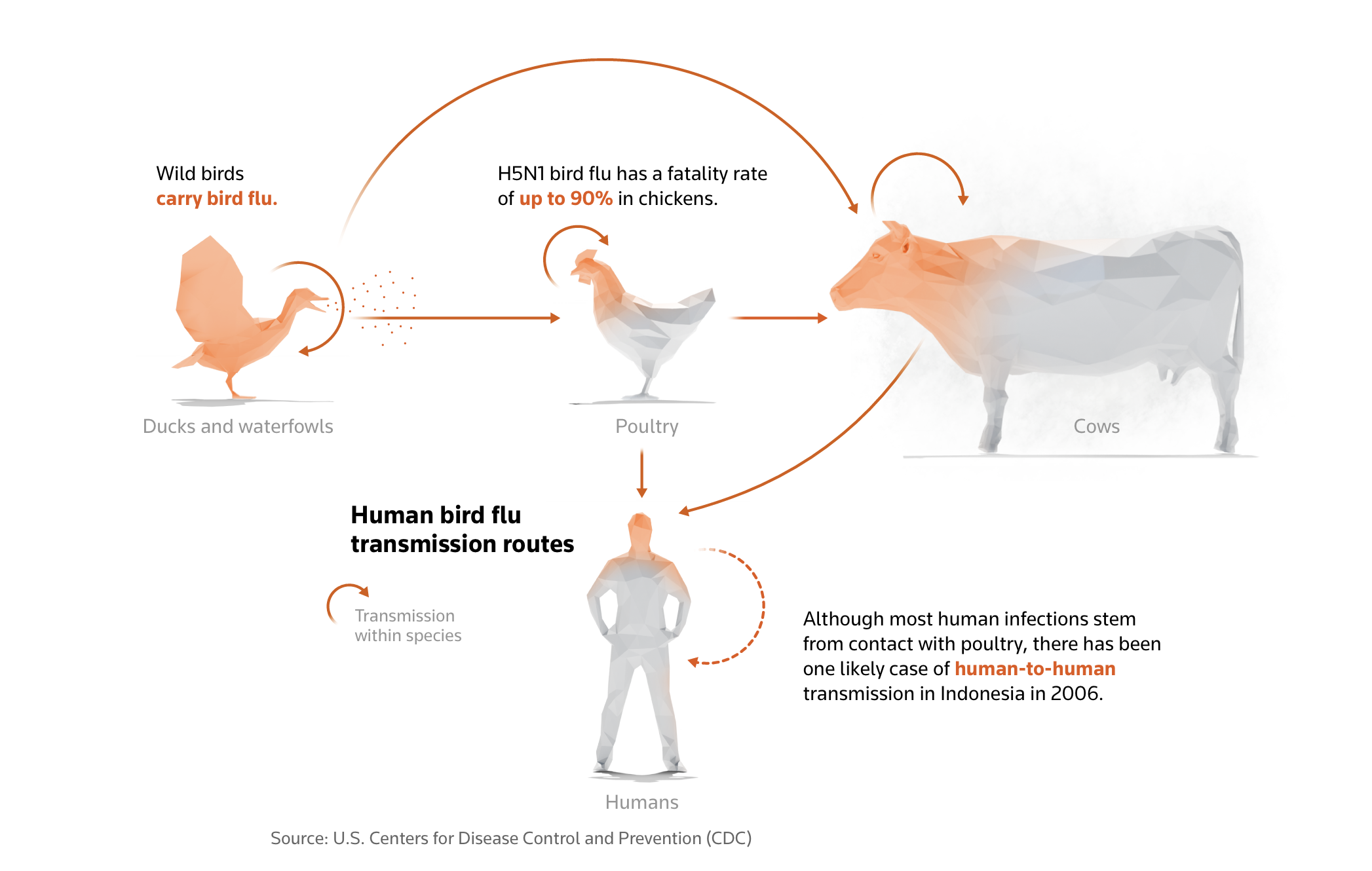
The unfold of fowl flu to an rising variety of species and its widening geographic attain have raised the dangers of people being contaminated by the virus, in accordance with the World Organisation for Animal Well being (WOAH).
The infections in cattle are from the identical subtype of fowl flu that has been infecting wild birds and poultry flocks globally, additionally killing a number of mammal species that probably contracted the virus from consuming sick or lifeless birds.
In February, a lethal kind of fowl flu was confirmed on the mainland of Antarctica for the primary time. Scientists mentioned it created a possible threat for the southern area’s enormous penguin colonies.
Since H5N1 arrived in South America in 2022, fowl flu had already killed dolphins, some 50,000 seals and sea lions alongside the coasts, and no less than half one million birds, in Chile and Peru.

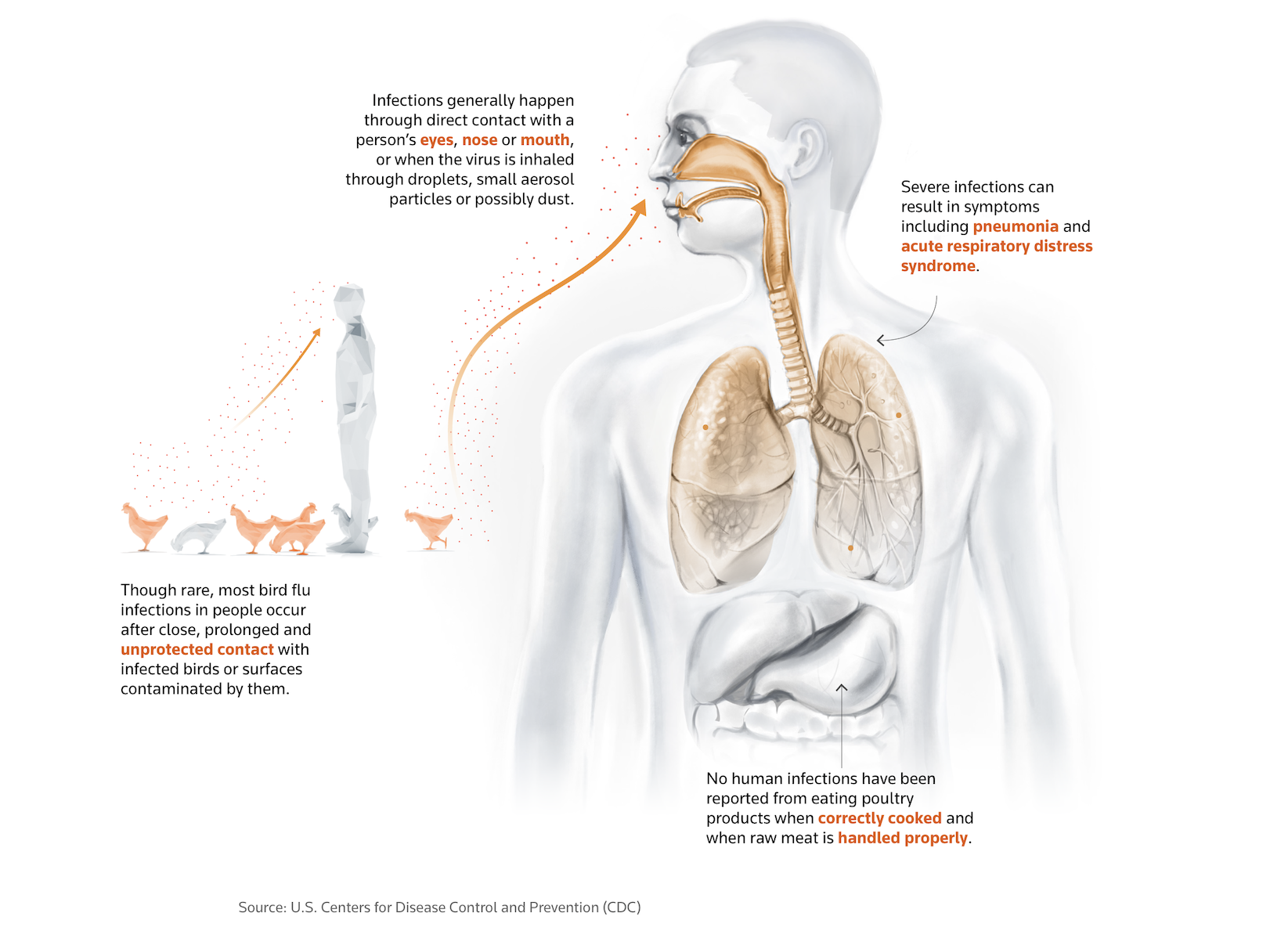
Whereas fowl flu infections in people are uncommon, they are often lethal after they occur. In keeping with the World Well being Group (WHO), there have been 889 H5N1 infections in people from 2003 to 2024. Of these, 463 or 52% resulted in dying.
US officers have strengthened measures to include the additional unfold of the primary recognized outbreak of H5N1 in dairy cows, which has now unfold to herds in 9 states and from there into the nation’s milk provide.
To this point there may be proof of untamed bird-to-cow, cow-to-cow, cow-to-poultry, and one case of cow-to-human transmission. There isn’t a proof of human-to-human transmission.
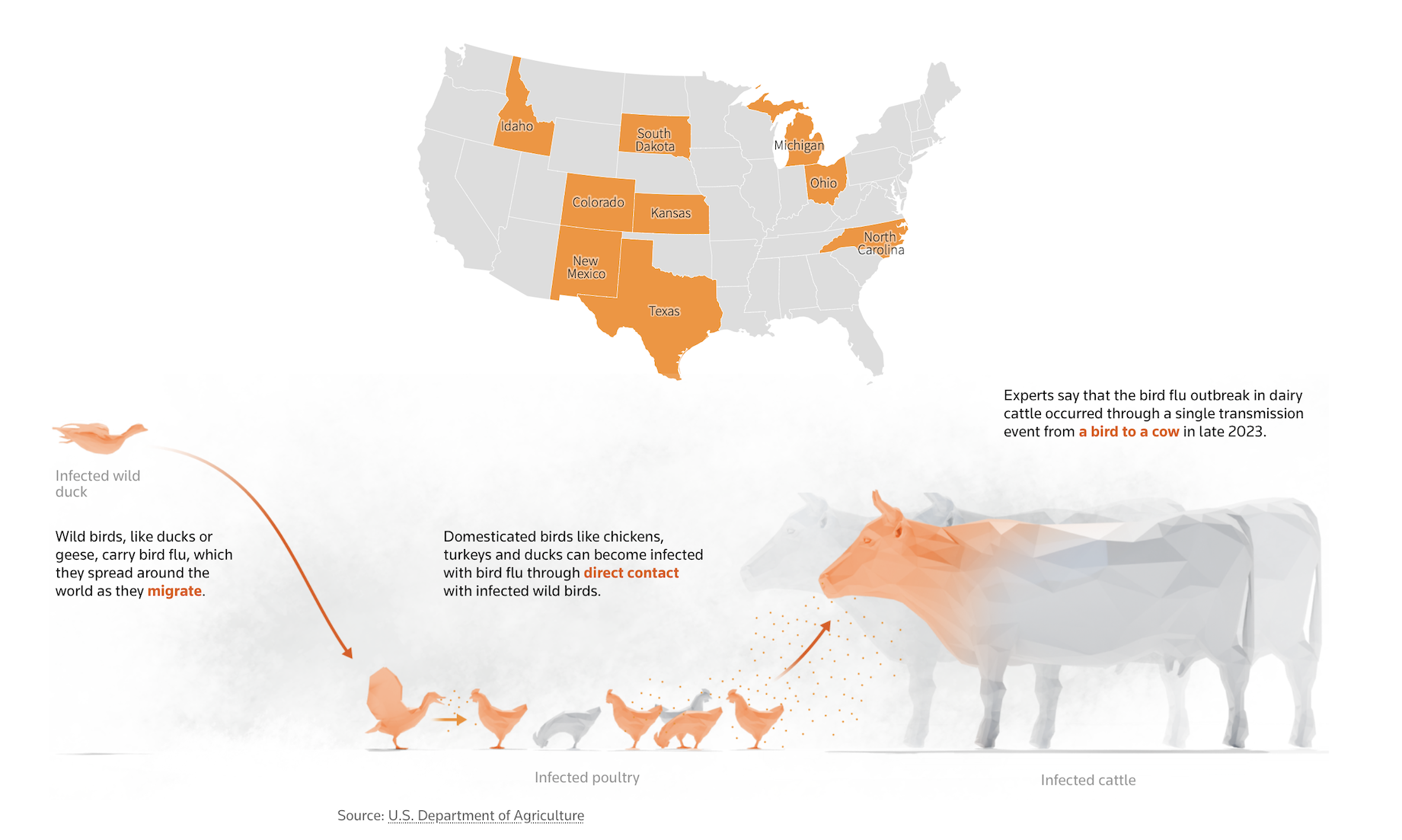
Due to the heavy viral load in milk and mammary glands, scientists suspect the virus can unfold between cattle through the milking course of, both by means of contact with contaminated tools or with virus that turns into aerosolised throughout cleansing procedures.
One in 5 business milk samples examined in a nationwide survey contained particles of the H5N1 virus, in accordance with the FDA. The company mentioned, although, there is no such thing as a motive to consider the virus present in milk poses a threat to human well being and that pasteurisation successfully killed the virus.
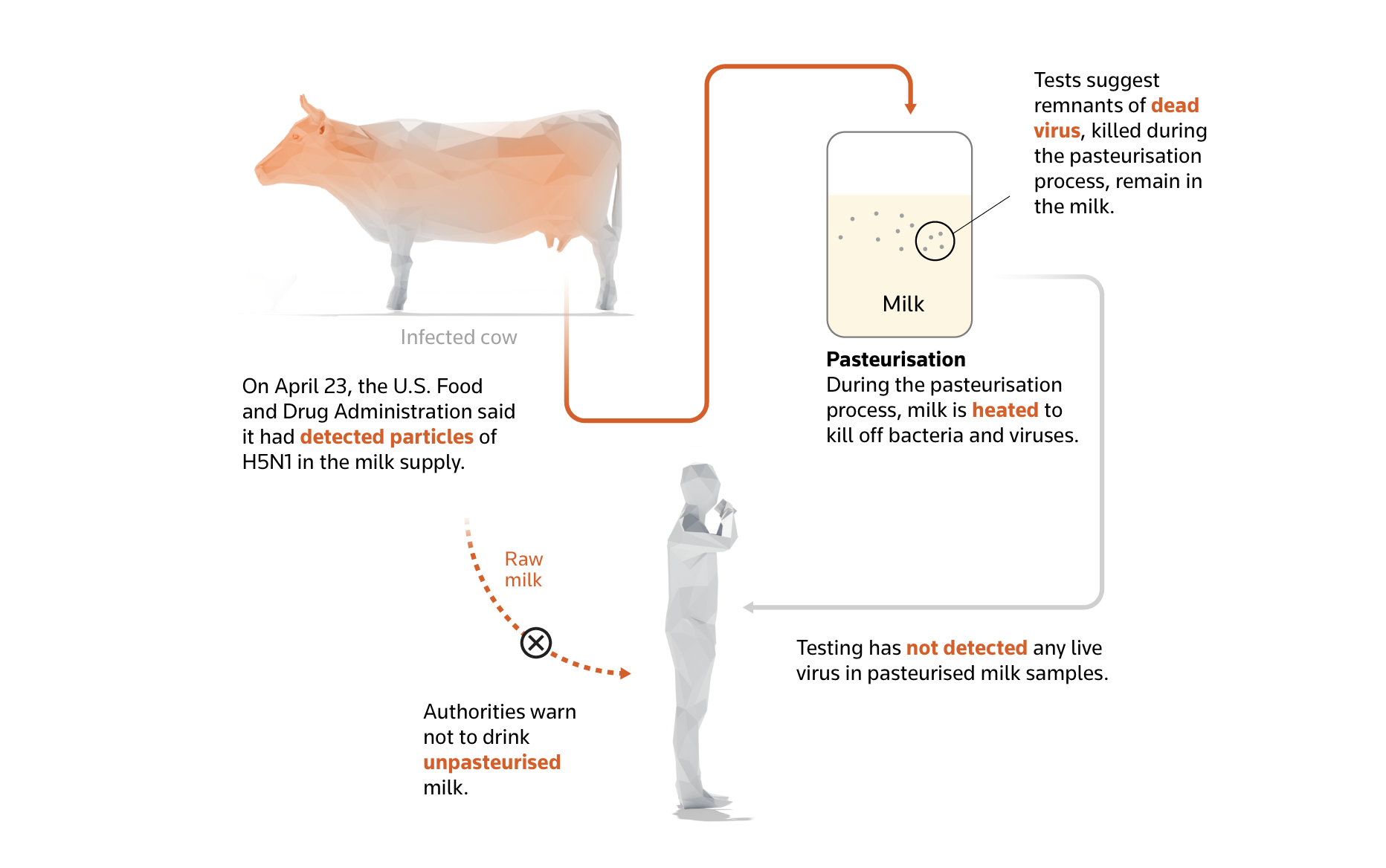
“I’m not fearful concerning the milk itself,” mentioned Samuel Alcaine, affiliate professor, of meals science at Cornell College. “It does point out that the virus is extra widespread amongst dairies than we had beforehand thought.”
A World Well being Group official mentioned there was a threat of H5N1 fowl flu virus spreading to cows in different international locations past the USA by means of migratory birds.


