A brand new mosasaur taxon from the Late Cretaceous of Morocco has been scientifically described. Khinjaria acuta was so long as an Orca (Orcinus orca). It had a sturdy cranium, sturdy jaws and dagger-like enamel. The researchers distinction right this moment’s marine ecosystems with few apex predators, with the Late Cretaceous marine surroundings. Writing within the journal “Cretaceous Analysis” the researchers painting an historic marine ecosystem teeming with predators.
Khinjaria acuta
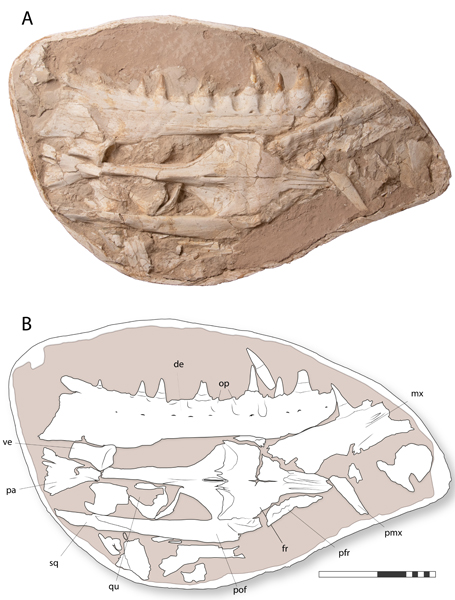
The research relies on a cranium and components of the postcranial skeleton collected from a phosphate mine southeast of Casablanca (Morocco). Researchers from the College of Tub, the Marrakech Museum of Pure Historical past, the Museum Nationwide d’ Histoire Naturelle (NMNH) in Paris (France), Southern Methodist College in Texas (USA), and the College of the Basque Nation (Bilbao) had been concerned.
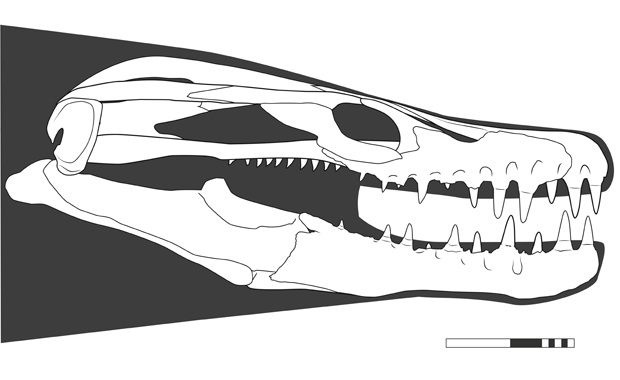
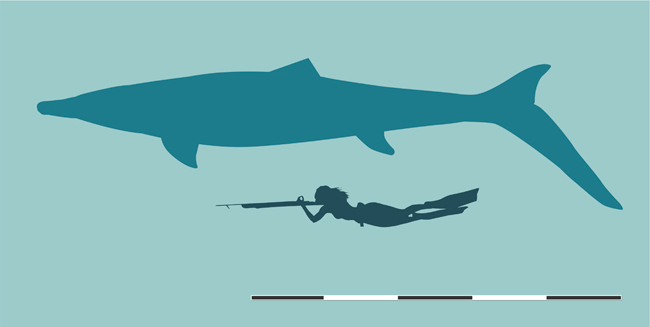
Measuring round eight metres in size, Khinjaria used its lengthy, dagger-like enamel to grab prey. It was a part of a very numerous fauna of predators that inhabited the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Morocco through the Maastrichtian faunal stage of the Late Cretaceous.
The Sheer Variety of High Predators within the Marine Ecosystem
One of many authors of the scientific paper, Dr Nick Longrich (College of Tub), acknowledged:
“What’s exceptional right here is the sheer range of high predators. Now we have a number of species rising bigger than an awesome white shark, and so they’re high predators, however all of them have completely different enamel, suggesting they’re looking in numerous methods.”
Dr Longrich added:
“Some mosasaurs had enamel to pierce prey, others to chop, tear, or crush. Now we’ve Khinjaria, with a brief face full of big, dagger-shaped enamel. This is without doubt one of the most numerous marine faunas seen anyplace, at any time in historical past, and it existed simply earlier than the marine reptiles and the dinosaurs went extinct.”
A Variety of Moroccan Marine Reptiles
Fossil discoveries have highlighted the astonishing range of enormous marine reptiles within the surroundings. Their completely different dentition means that many weren’t straight competing, that area of interest partitioning was occurring. For instance, the researchers performed a phylogenetic evaluation and positioned Khinjaria in a mosasaur clade which they named the Selmasaurini. Additionally positioned on this clade was the Moroccan plioplatecarpine mosasaur Gavialimimus almaghribensis. This mosasaur was a specialised fish hunter.
To learn Every part Dinosaur’s article about Gavialimimus almaghribensis: A New Species of Mosasaur from Morocco.
Mosasaurs, plesiosaurs and large sea turtles disappeared, together with total households of fish on the finish of the Cretaceous. This led to the evolution of recent marine ecosystems with whales and seals as apex predators together with teleost fish equivalent to swordfish and tuna.
Dr Longrich commented:
“There appears to have been an enormous change within the ecosystem construction up to now 66 million years. This unimaginable range of high predators within the Late Cretaceous is uncommon, and we don’t see that in fashionable marine communities.”
An Ecosystem Totally different from a Trendy Marine Ecosystem
Trendy marine meals chains have only a few massive apex predators, animals like orcas, white sharks, and leopard seals. The Late Cretaceous had many extra kinds of marine predators.
Dr Longrich continued:
“Trendy ecosystems have predators like baleen whales and dolphins that eat small prey, and never many issues consuming massive prey. The Cretaceous has an enormous variety of marine reptile species that take massive prey. Whether or not there’s one thing about marine reptiles that prompted the ecosystem to be completely different, or the prey, or maybe the surroundings, we don’t know. However this was an extremely harmful time to be a fish, a sea turtle, or perhaps a marine reptile.”
Professor Nathalie Bardet, (Pure Historical past Museum of Paris), defined:
“The Phosphates of Morocco deposit in a shallow and heat epicontinental sea, below a system of upwellings; these zones are attributable to currents of deep, chilly, nutrient-rich waters rising in direction of the floor, offering meals for big numbers of sea creatures and, consequently, supporting a number of predators. That is in all probability one of many explanations for this extraordinary paleobiodiversity noticed in Morocco on the finish of the Cretaceous.”.
The phosphate mines of Morocco have supplied a wealth of marine fossil materials. The specimens collected embody the “saw-toothed” mosasaur Xenodens, Stelladens which had enamel with extra reducing edges and Thalassotitan whose enamel had been conical in form and large.
Every part Dinosaur acknowledges the help of a media launch from the College of Tub within the compilation of this text.
The scientific paper: “A weird new plioplatecarpine mosasaurid from the Maastrichtian of Morocco” by Nicholas R. Longrich, Michael J. Polcyn, Nour-Eddine Jalil, Xabier Pereda-Suberbiola and Nathalie Bardet printed in Cretaceous Analysis.
Check out the Every part Dinosaur web site: Every part Dinosaur.



