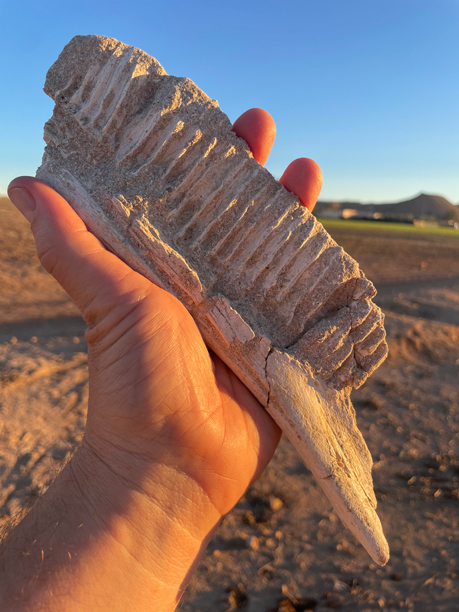
A brand new, pony-sized Moroccan lambeosaurine dinosaur has been named and described. The brand new dinosaur has been named Minqaria bata. It intently resembles the one beforehand recognized African duckbill, Ajnabia odysseus. Nonetheless, the form of the jaws and enamel are distinctive, demonstrating it was a definite species. Minqaria most likely occupied a special ecological area of interest.

Minqaria bata – (Arabic for “Beak” and “Duck” Respectively)
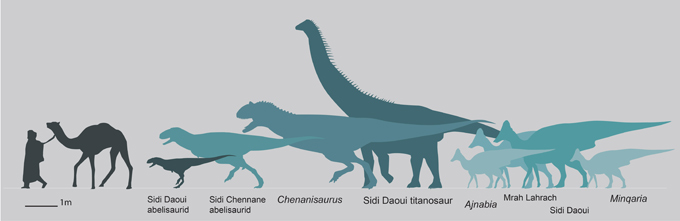
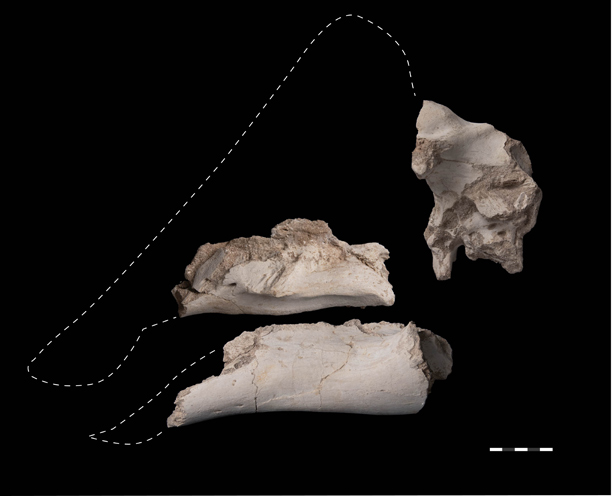
The fossils consisting of a proper maxilla with enamel, a partial left dentary and the braincase come from marine phosphate deposits positioned at Sidi Chennane within the Oulad Abdoun Basin. The dimensions of the fossils, the related matrix and the dearth of duplication of components means that these fossils got here from a single, mature dinosaur. They signify a dwarf duck-billed dinosaur, a Late Cretaceous lambeosaurine that was smaller than Ajnabia odysseus, the primary hadrosaurid recognized from Africa (Longrich et al, 2020). M. bata is estimated to have been round 3.5 metres in size and weighed roughly 250 kilograms.
To learn Every thing Dinosaur’s 2020 weblog publish about Ajnabia odysseus: The First Hadrosaurid Dinosaur from Africa.
The genus title is derived from the Arabic “minqar” which implies beak and the species title is from the Arabic “bata” for duck.

The Variety of North African Lambeosaurines
A humerus and femur additionally described within the scientific paper seem to signify lambeosaurines too. Nonetheless, their dimension signifies that bigger lambeosaurines, animals longer than six metres in size have been additionally current within the ecosystem.
The invention of Ajnabia in 2020 was stunning. Throughout the Late Cretaceous, a whole lot of miles of water separated North Africa from Eurasia. The brand new lambeosaurine fossils not solely affirm the existence of lambeosaurines in North Africa, however exhibits they have been numerous, with at the least 4 taxa current.
How Did Duck-billed Dinosaurs Get to North Africa?
This new research revealed within the journal “Scientific Studies” reveals that not solely did duckbills handle to cross the Tethys Sea, however they turned extremely numerous as soon as they colonised Africa. The duck-billed dinosaurs are thought to have advanced in North America. Africa throughout the Late Cretaceous was an remoted continent, surrounded on all sides by water. So, how did duckbill dinosaurs, a bunch that advanced in North America, find yourself in Morocco?
Anatomical traits of Minqaria are much like European hadrosaurs. The researchers postulate that duckbills both swam or floated throughout a number of hundred kilometres of open water to colonise Africa.
Dr Nick Longrich (College of Bathtub), who led the research commented:
“These have been most likely loud, vocal animals. Trendy birds vocalise to search out mates, or to declare territories. However they’re particularly vocal in flocks – a flock of flamingos or a nesting colony of pelicans is extraordinarily noisy, continually speaking. So, it’s doubtless that like birds, these duckbills have been social animals.”
Social Dinosaurs
The mind can be giant by dinosaur requirements, a function related to social animals like crows and primates.
Dr Longrich defined:
“There have been most likely very loud, noisy herds – or flocks in case you favor – of those little duckbills wandering the coasts of Morocco 66 million years in the past.”
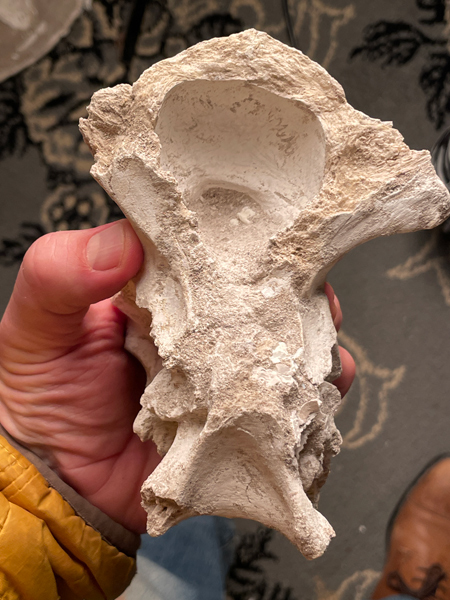

Commenting on the presence of lambeosaurine dinosaurs on the remoted continent of Africa, Dr Longrich added:
“Not solely did duckbills handle to succeed in Africa on the finish of the Cretaceous, however as soon as they did, they rapidly advanced to reap the benefits of open niches and have become numerous.”
Analogies could be discovered within the fashionable world. Animals can generally make sudden and strange journeys throughout giant our bodies of water. Throughout the Ice Age, elephants, deer and hippos have been in a position to cross the Mediterranean Sea to succeed in the island of Crete. Iguanas swept offshore by a hurricane could be transported a whole lot of miles to different Caribbean islands as they cling to dislodged vegetation.
Dr Longrich acknowledged:
“It’s extraordinarily inconceivable that dinosaurs may cross water to get to Africa, however inconceivable isn’t the identical as unimaginable. And given sufficient time, inconceivable issues turn into possible. Purchase a lottery ticket every single day, and in case you wait lengthy sufficient, you’ll win. These ocean crossings is likely to be once-in-a-million-year occasions however the Cretaceous lasted almost 100 million years. Loads of unusual issues will occur in that point – together with dinosaurs crossing seas.”
Outstanding to Uncover Fossils of Hadrosaurs Like Minqaria bata in Africa
Co-author Dr Nour-Eddine Jalil (Pure Historical past Museum of Paris and the Université Cadi Ayyad in Morocco) commented:
“Minqaria and its kinfolk are gamers that just a few years in the past we’d by no means have presupposed to be on the African continent at the moment.”
The physician added:
“The phosphates of Morocco gives new photographs on previous biodiversity in a key interval of the historical past of life, the final moments of the dinosaur age adopted by the diversification of mammals, saying a brand new period. Regardless of their marine origin, these phosphates of Morocco additionally include stays of vertebrates that lived on land. They represent one of many solely home windows on the terrestrial ecosystems in Africa. The dinosaur stays recommend an awesome range, all of the three main teams of dinosaurs are represented, the abelisaurid carnivores and the sauropod and ornithischian herbivores.”
Every thing Dinosaur acknowledges the help of a media launch from the College of Bathtub within the compilation of this text.
The scientific paper: “A brand new small duckbilled dinosaur (Hadrosauridae: Lambeosaurinae) from Morocco and dinosaur range within the late Maastrichtian of North Africa” by Nicholas R. Longrich, Xabier Pereda-Suberbiola, Nathalie Bardet and Nour-Eddine Jalil revealed in Scientific Studies.
The Every thing Dinosaur web site: Every thing Dinosaur.