Why is the GH10 household of xylanases more practical?
Among the many enzymes that play a crucial function in optimizing animal diet, xylanase is extensively acknowledged for its capability to interrupt down complicated polysaccharides in plant-based feed substances, bettering nutrient utilization and total animal efficiency. Nonetheless, in current a long time, regardless of advances in manufacturing, processing applied sciences, and utilization of by-products, xylanase enzyme expertise has lagged behind, particularly in flexibility required for contemporary weight loss plan formulation.
Xylanase targets xylan, a serious part of hemicellulose present in plant cell partitions. It’s generally utilized in animal diet to boost the digestibility of dietary fiber, significantly in monogastric animals corresponding to poultry and swine. Plant-based feed substances, corresponding to corn, wheat, and soybean meal, are wealthy in non-starch polysaccharides (NSPs), together with arabinoxylans, that are tough for animals to digest effectively.
Xylanase helps break down these complicated NSPs, releasing extra easy sugars and different vitamins for absorption within the digestive tract. This not solely improves feed effectivity but in addition reduces the anti-nutritional results of NSPs, corresponding to intestine viscosity and elevated microbial fermentation, which might result in digestive problems and lowered animal efficiency.
GH10 xylanases make it attainable to include greater ranges of cost-effective substances
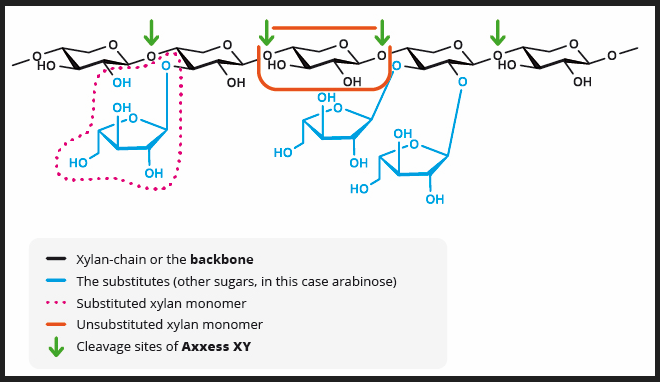
Whereas the GH11 household of xylanases, generally employed in feed, successfully lowers viscosity ranges in broiler gastrointestinal tracts by lowering soluble NSPs in wheat-based diets, they show much less efficient when confronted with the extra complicated arabinoxylan spine of insoluble NSPs.
The 3D construction of GH11 xylanase explains its limitations. GH11 xylanases require 3-4 consecutive unsubstituted xylan monomers on the spine to find an energetic website, making them much less efficient within the presence of aspect chains on arabinose backbones. They’re extremely particular, favoring low-branching wheat backbones.
In distinction, GH10 xylanases, although not generally utilized in feed, provide a definite benefit. They require solely two or fewer consecutive unsubstituted xylan monomers to seek out an energetic website, enabling them to behave on xylose residues close to branches. This ends in extra and shorter xylo-oligomers than GH11 xylanases produce. Merely put, GH10 xylanases have a shallower cleft, offering larger catalytic versatility (Pollet 2010).
This versatility permits for a broader vary of feed substances, together with co- and by-products, whereas sustaining efficiency. Subsequently, GH10 xylanases make it attainable to include greater ranges of cost-effective substances, presenting a big alternative to scale back total feed prices.
Why is the GH10 household of xylanases more practical?
Substrate Specificity: GH10 xylanases are likely to exhibit a broader substrate specificity in comparison with GH11 xylanases. They’ll effectively hydrolyze a wider vary of xylan constructions present in varied plant cell partitions. This broader specificity permits for higher degradation of several types of dietary fiber current in animal feed substances.
Enhanced Thermal Stability: GH10 xylanases typically reveal higher warmth resistance, which is essential within the feed manufacturing course of. The flexibility to resist greater temperatures throughout feed processing, corresponding to pelleting or extrusion, ensures that the enzyme stays energetic and efficient all through all the manufacturing cycle.
Improved pH Tolerance: GH10 xylanases could have higher pH tolerance, permitting them to operate optimally within the numerous pH situations of the digestive tract. This will result in improved enzyme exercise and larger effectivity in breaking down xylan within the animal’s gastrointestinal system.
Increased Catalytic Effectivity: GH10 xylanases are identified for his or her greater catalytic effectivity, which means they will break down xylan molecules extra quickly and successfully. This results in higher utilization of vitamins within the feed, improved feed conversion, and enhanced animal efficiency.
Resistance to Protease Inhibition: In some circumstances, GH11 xylanases could also be inhibited by the presence of proteases or different enzymes within the digestive system. GH10 xylanases are sometimes extra immune to such inhibitory results, guaranteeing their continued exercise within the intestine.
Broader Software Vary: Attributable to their versatility and improved efficiency beneath varied situations, GH10 xylanases are higher fitted to a variety of feed formulations and animal species, making them a extra versatile selection for business nutritionists.
Current improvements in enzyme expertise have additional improved the effectiveness of xylanase and different enzymes in animal diet. Custom-made enzyme options, heat-stable xylanases, enzyme mixtures, molecular genetics, and nutrigenomics are all contributing to the development of precision diet in animal manufacturing. As these improvements proceed to evolve, they maintain the promise of additional optimizing animal efficiency and sustainability within the livestock and poultry industries.


